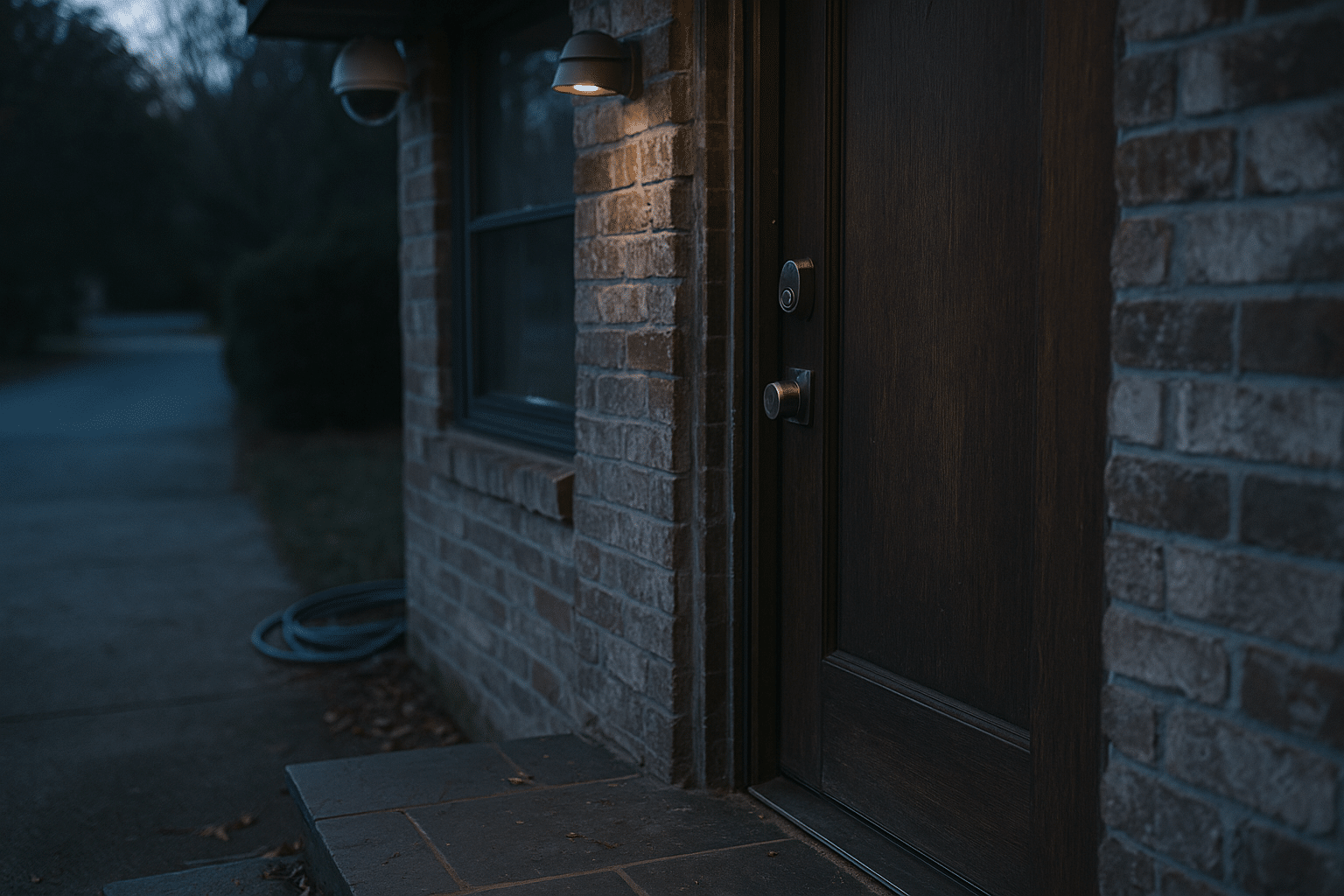
Essential Home Security Tips for Every Homeowner
Why Home Security Matters + Outline of This Guide
Home security is not a single gadget; it’s a system with layers that work together to reduce risk, provide timely alerts, and document events. The three pillars—surveillance, alarm systems, and smart locks—each serve different roles: see what’s happening, trigger a response, and control access. When combined thoughtfully, they can discourage opportunistic intrusions, shorten response times, and make daily life more convenient without inviting privacy headaches. This section explains what we’ll cover and why each piece matters, so you can pick a path that matches your home, habits, and budget.
Here’s the outline you’ll follow:
– Surveillance: camera types, placement, retention, and analytics for clarity without clutter.
– Alarm Systems: monitored vs. self-monitored, sensor strategy, and false-alarm reduction.
– Smart Locks: access methods, hardware choices, and real-world risks to plan around.
– Integration & Privacy: tying systems together, networking basics, and data discipline.
– Action Plan & Budgeting: phased rollouts, maintenance, and a homeowner-focused conclusion.
Why this matters now: more connected devices means more capability—and more decisions. Cameras have improved dynamic range and smarter detection, alarms can use multiple communication paths, and locks can grant temporary codes to guests or tradespeople without handing over a physical key. Yet thoughtful setup still beats raw specs. A well-placed 1080p camera can outperform a poorly positioned higher-resolution model; a right-sized sensor layout can cut false alarms; and a sturdy door and frame can turn a fancy lock into a reliable barrier instead of a fragile showpiece. Throughout, you’ll find practical guidelines, comparisons, and examples designed to work in ordinary homes, not just ideal lab conditions. By the end, you’ll have a blueprint to build security in layers, manage costs sensibly, and keep control of your data—not the other way around.
Surveillance: Seeing Clearly Without Oversharing
Surveillance earns its keep when it delivers useful visibility while respecting privacy and storage limits. Start with coverage goals before gear: front entry, secondary doors, driveway, and the backyard gate are common priorities. Interior cameras can watch shared spaces—like a hallway or main room—but many households avoid private rooms for comfort and privacy. Think of cameras as storytellers: they should capture faces at entries, license plates as vehicles approach, and wide context in areas where movement often begins.
Key choices to weigh:
– Power and connectivity: wired lines provide steady power and consistent bandwidth; wire-free options trade endurance for flexibility and easy installation.
– Image quality: 1080p is often sufficient for identification at close range; higher resolution helps with detail at distance but increases storage and bandwidth needs.
– Night performance: look for strong low-light capture and balanced exposure so faces aren’t lost to glare from porch lights or headlights.
Placement matters more than pure specs. Mount entry cameras near head height but secure from tampering; angle them to minimize backlighting from bright skies. For driveways, a slightly elevated, off-angle view can capture both faces and vehicle details without relying on a tight, easily missed shot. Indoors, a camera aimed across an entry path can catch movement and context as someone moves through a pinch point. Add motion detection zones and sensitivity tuning so swaying trees or passing clouds don’t flood your timeline.
Storage strategy sets your retention and privacy posture. Local storage keeps footage on-site for faster access and fewer ongoing fees, but requires resilient power protection and a plan for off-site backups of critical clips. Cloud storage simplifies remote access and off-site safety yet consumes bandwidth and may raise privacy concerns. Hybrid approaches—local recording with selective cloud clips—strike a balance for many homes. Footage retention is often most useful for recent weeks; beyond that, consider archiving only notable events to keep libraries lean.
Analytics now do more than generic motion. Person and vehicle detection can reduce false alerts, while package detection can add practical value. Calibrate carefully: overly aggressive filters might miss important events; lax settings can create alert fatigue. Ethically, avoid pointing cameras into a neighbor’s yard or windows; frame for your property and shared public areas only. A visible yet modest camera presence can discourage opportunistic activity, and clear views of entries help document what matters if something does occur. The goal isn’t constant watching—it’s actionable clarity when you need it.
Alarm Systems: Layers, Reliability, and Fewer False Alarms
If surveillance helps you see, alarm systems help you respond. A solid alarm plan pairs perimeter sensors—door and window contacts—with interior motion detectors that watch hallways or large rooms. Glass-break sensors add coverage for windows that might be forced without opening. The control hub should support battery backup and at least two communication paths, such as broadband plus a cellular fallback, so an outage or a cut line doesn’t silence alerts. Loud sirens buy time by drawing attention and pressuring intruders to leave quickly.
Monitoring approaches differ in cost and control. Professional monitoring can summon help when you can’t answer your phone, while self-monitoring gives you direct control and lower ongoing costs but depends on your availability. Some homeowners choose a hybrid: professional monitoring during trips, self-monitoring otherwise. Whichever you choose, treat alarm permits and local regulations seriously to avoid fines and ensure timely responder access when needed.
False alarms are common—but manageable. Most stem from user error or poor sensor placement. Practical steps include:
– Entry/exit delays that match real movement from door to keypad.
– Cross-zoning or multi-sensor confirmation before dispatch on select zones.
– Pet-immune motion detectors mounted at correct heights and angles.
– Periodic testing routines so weak batteries or failed sensors don’t surprise you.
– Distinct codes for household members and trusted visitors, with quick revocation when access changes.
A thoughtful notification plan prevents alert fatigue. Prioritize critical triggers like forced entry or smoke detection (if integrated), then add secondary alerts—such as a garage door opening—only if they inform real action. Map alerts to time-of-day: a window sensor at 2 a.m. is different from the same event on a breezy afternoon when windows are often open. Logs and simple weekly tests help you confirm reliability, and many systems can report sensor battery levels so replacements are timely rather than urgent.
Finally, align alarms with daily life. If you frequently host guests or tradespeople, create temporary codes or schedules rather than sharing permanent ones. If you rarely use certain doors, place louder chimes or stricter rules on those entries. And if you travel, set up a neighbor notification plan in addition to monitoring, ensuring someone local can check a door, move a package, or meet responders if needed. When alarms are tuned to your routines, they work with you instead of nagging you.
Smart Locks: Access Control That Works in the Real World
Smart locks turn doorways into managed checkpoints without making daily entry a chore. Start with the door itself: a lock is only as strong as the door slab, frame, and strike plate. Reinforcing plates and long screws that bite into framing can raise the effort needed to force entry, turning quick kicks into noisy, time-consuming attempts. With that baseline in place, your smart lock choice becomes about access options, reliability, and privacy.
Consider how you prefer to unlock: keypad codes, traditional keys, fobs or cards, or phone-based credentials. Keypads are flexible for families and guests, and temporary codes simplify short-term access for cleaners or maintenance. Phone credentials can be convenient, especially when paired with proximity-based unlocking, but set conservative rules so doors don’t open prematurely. Automatic relock can protect against forgetfulness; balance that with a reasonable auto-lock delay so you aren’t locked out while unloading groceries.
Security features deserve a close look. Favor strong encryption for lock-to-hub and app communications, lockout thresholds after repeated failed attempts, tamper alerts, and a clear log of access events you control. Choose models with replaceable batteries and clear low-power warnings; keep a backup key or portable battery method in case power runs low at a bad time. Mechanical durability matters just as much as software: a solid metal housing, hardened fasteners, and a robust deadbolt throw help the lock resist prying and torque.
Privacy and account hygiene are essential. Limit shared app access to people who truly need it; give guests time-bound codes instead of permanent ones. When someone moves out or no longer needs entry, revoke credentials immediately. Avoid saving master codes in notes or messages; store them in a secure manager and keep a paper backup in a safe place within the home. If remote access is available, enable two-factor authentication and notifications when new devices sign in.
Door context brings smart features to life. For example, link a lock and an entry camera so the camera bookmarks a short clip whenever a code is used. Or pair a lock with an interior hallway light during evening hours, making the entry feel safe and well-lit as you step inside. Treat these as quality-of-life enhancements rather than absolute security controls. With sturdy physical components, predictable access rules, and conservative remote privileges, smart locks can deliver daily convenience without raising your risk.
Bringing It Together: Integration, Privacy, Budget, and Next Steps
Security works best as a cohesive routine rather than a pile of disconnected devices. Integration begins with simple, reliable automations: arm the alarm’s stay mode at night; disarm via a code that also logs the front camera clip; turn on an entry light when a door opens after sunset. Keep automations legible—use names and schedules you can understand at a glance—and test them slowly so surprises don’t creep into your daily rhythm.
Network and data hygiene add staying power. Place connected devices on a separate home network, use unique strong passwords, and enable two-factor authentication wherever possible. Update firmware on a schedule and prefer local control for routine tasks, reserving remote access for cases where it truly helps. For video, apply data minimization: retain clips that matter, archive noteworthy events, and let day-to-day noise expire. If you share clips with neighbors or community groups, blur sensitive areas and avoid revealing daily patterns like exact commute times.
Budgeting can be phased to avoid big up-front costs. A practical starter path might look like this:
– Phase 1: reinforce doors and frames, add contacts to primary entries, and install one well-placed entry camera.
– Phase 2: expand to secondary doors and key windows, add a motion detector to a central interior path, and tune alerts for signal over noise.
– Phase 3: introduce a smart lock at the main entry, apply temporary codes for guests, and link a camera clip to each access event.
– Phase 4: layer in secondary cameras or specialized sensors as gaps appear, then revisit storage and retention policies.
Measure progress by outcomes: fewer false alarms, clearer identification on footage, faster arming and disarming, and a household that can operate the system confidently. Review every six months: walk the perimeter, check mounting points, replace aging batteries, and test every sensor. Keep a short written playbook—codes, contact numbers, and shutdown steps—in a secure location for others to use if you’re unavailable.
Conclusion for homeowners: think in layers, choose features that match real habits, and value reliability over novelty. Surveillance provides clarity, alarms coordinate response, and smart locks make access predictable and shareable. When these pieces are tuned to your space and schedule—and when privacy and maintenance get the attention they deserve—you create a home that feels calm, prepared, and welcoming. Start small, improve steadily, and let results guide the next upgrade rather than hype. That steady approach pays dividends every day, not only on the rare day you truly need it.